

Some of these trends include atomic size, ionization energy, electronegativity, density. C O, N O, N 2 O ).Īmphoteric oxides behave as acidic with bases and as basic with acids, whereas neutral oxides have no acidic or basic properties. General trends exist within groups and periods on the periodic table. Oxides of elements in the centre are amphoteric. The element on extreme right is the most acidic. Group - reactivity decreases as you go down the group. Group - reactivity increases as you go down a group In Non-metals Period - reactivity increases as you go from the left to the right. The normal oxide formed by the element on extreme left is the most basic. In general, elements in the same column display similar chemical properties, possibly smoothly changing along the column, while along a period there is a. 1 Answer Abdul Sammad In Metals: Period - reactivity decreases as you go from left to right. (3) Reactivity with Oxygen : Elements on two extremes of a period easily combine with oxygen to from oxides.

(2) Metallic and non-metallic Properties : We move left to right in a period metallic property decreases and non-metallic property increases. (1) Reactivity of Oxidation and Reduction : Extremely left elements of periodic table are reducing agent and extremely right elements of periodic table are oxidising agent. (Exception : Noble gas)Įlements are more reactive in both of the side and elements are less reactive in middle in periodic table.Įlements are situated very left side (Alkali metals) have tendency to lose one electron and elements are situated right side (Halogen) have tendency to gain one electron and becomes negative. The reactivity decreases as you go across the period because: The outer electrons are all roughly the same distance away from the nucleus. So, we can say that in period ionisation enthalpy is very less in left side and electron gain enthalpy is very high and negative in right side. This is an extension of the periodic trend that the energy required to remove an electron increases going across a row of the periodic table. So, ionisation enthalpy increases in period and value of electron gain enthalpy becomes more negative. And the farther they are from the righ side of the table, the weaker their electronegativity is, resulting in lower Chemical Reactivity.When we go left to right atomic radius and ionic radius decreases. That is why as you go up a group Chemical Reactivity increases because it is easier for elements to gain electrons when they have high electronegativity. Chemical Reactivity decrease as you go down the groupįor Non-Metals, the farther right-up in the table you go, the higher the electronegativity.Chemical Reactivity increases as you go left to right of the periodic table.And you go from left to right on the periodic table elements have more electrons in their valence shells they have to get rid off which requires an element to have high energies which results into lower Chemical Reactivity.
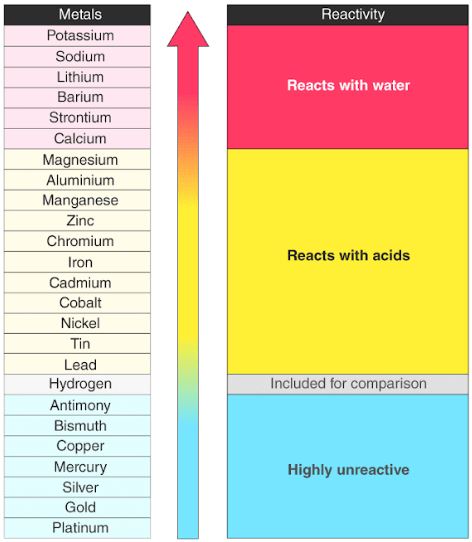
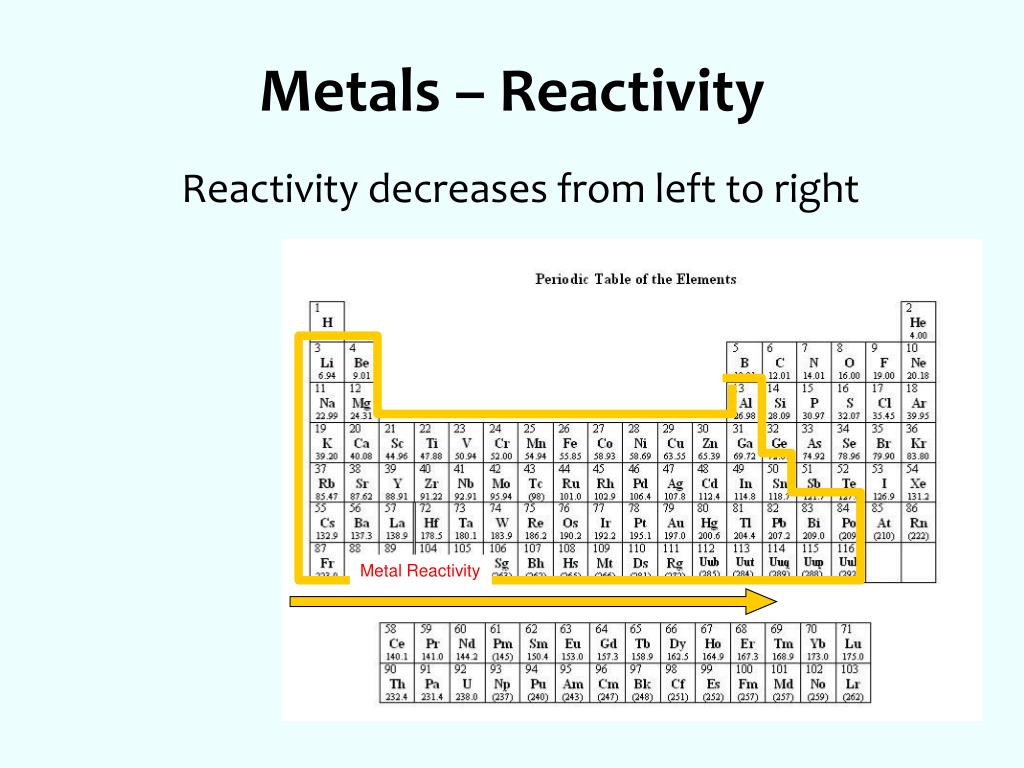
This happens because as you go down a group, it is easier for electrons to be taken or given away, resulting in high Chemical Reactivity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
